Return to Pogu Michele's personal page
The purpose of this work is the development of a docking method for an off-road mobile robot. The goal is the accurate determination of the robot pose relative to the docking station, in order to control the robot during the docking.
The first approach will rely on a QR code positioned at a known position on the docking station and its observation by a robot camera.
Then we will aim to exploit the joint presence of more than one QR code, jointly observed by the robot camera.
The last step, if time will allow, will be to evaluate pose of the robot w.r.t. the docking station without QR codes, but exploiting the 3D model of the docking station and the point cloud observed from the robot 3D camera.
The pose estimation system shows the 6 degrees of freedom of the QR Code relative to the camera. The 3 degrees of freedom indicating the position are expressed in meters, while the orientation is expressed according to the Euler angles in Roll, Pitch, and Yaw in radians. We used the OpenCV library. In the first phase, we calibrated the camera using a chessboard, which, through projections, calculated the camera matrix and distortion coefficients. Later, after passing these parameters to the pose estimation function, we were able to calculate the position and orientation. The latter was initially expressed with a vector indicating the axis of rotation and its norm representing the angle.Subsequently, we calculated the ground truth to estimate the software's precision error and the quality of the data. We noticed that as the distance increased, the error also increased, and that the best lighting for pose estimation is white and cold light.
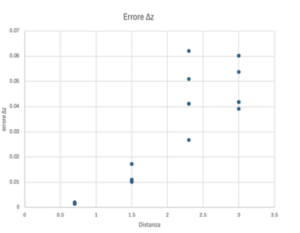
The results of the experiment showed an interesting trend regarding the measurement errors. It was found that as the distance between the camera and the QR code increased, the error in the detected positions also increased. This is likely due to the decreased resolution and accuracy of the vision system as the QR code moves farther away from the camera
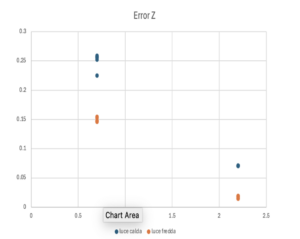
Additionally, it was observed that using white light significantly improved the accuracy of the positions detected by the software. White light provides more uniform lighting, allowing the camera to capture more detailed images, thus reducing detection errors and enhancing the overall measurement quality.
